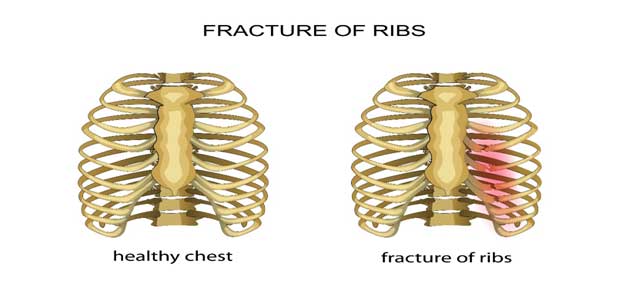
Anatomy of the ribs
Rib fractures tend to occur from traumatic falls. I’ve taken care of many elderly patients with fractured ribs. Most of these falls occur from slipping in the bathtub and hitting their ribs on the edge of the tub. Patients complain of intense, severe pain and difficulty taking deep breathes. Elderly patients who have difficulty breathing should be monitored for atelectasis and pneumonia. Pain can last for several weeks. Elderly patients are at an increased risk of death due to complications. Assessment: one or more ribs are very tender. Sometimes the fractured rib(s) can be felt by gently pressing on the injured area. A chest X-ray to assess damage to the lungs and a rib series to assess fractured ribs are necessary. Rib series X-rays are preferred over standard X-rays because standard X-rays do not always show fractures. Rib fractures can cause pulmonary contusions.
Surgery is not needed for most rib fractures. Treatment for managing the pain includes NSAIDS and lidocaine transdermal patches.Compression of the injured area with a pillow can minimize the pain while laughing, coughing, sneezing, and rising from a bed.
However, rib fractures can cause other serious injuries that do require surgery such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, hemopneumothorax, and pulmonary laceration(s).
References
Artemida-psy. (2020). Vector illustration of broken ribs chest thorax. [Illustration]. Retrieved from https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/vector-illustration-broken-ribs-chest-thorax-620986040.
Melendez, S. (2017). Rib Fracture. Retrieved from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/825981-overview
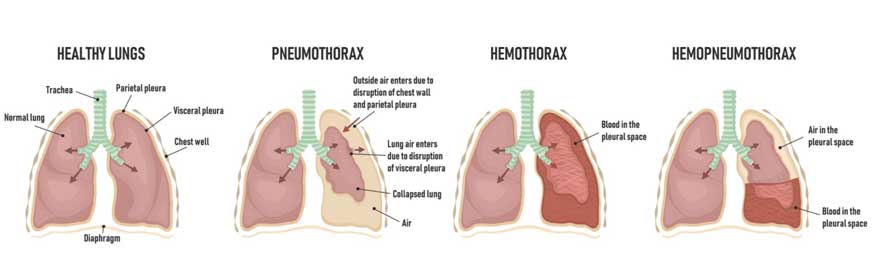
Hemothorax
There are other causes of a hemothorax, such as blood clotting defects, open heart surgery, pulmonary infarction, lung cancer, and tuberculosis (TB). However, this article focuses on traumatic causes.
Patients who present with a hemothorax will have increased anxiety because they have increased chest pain, increased heart rate, and rapid, shallow breathing. They may have shortness of breath. On assessment, health providers will hear diminished or absent breath sounds from the affected lung. Patients may have low blood pressure that may cause the organs to not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which may result in shock, pale skin complexion, cool, and clammy skin.
To assess the patient for a hemothorax, a chest X-ray, a CT scan, and a possible thoracentesis (the draining of pleural fluid with a needle)will be ordered. The best treatment plan is to treat the underlying causes for a collapsed lung. Stabilize the patient, stop the bleeding, and remove blood from the pleural space by inserting a chest tube through the chest wall between the ribs. The chest tube remains in place until the lung has re-expanded.If bleeding does not stop, surgery (thoracotomy) may be needed to stop the bleeding.
Prognosis depends on the seriousness of the trauma that caused the hemothorax, the amount of blood loss, and the quickness with which the patient can be stabilized.
References
Logika600. (2020). Human lungs with pneumothorax, hemothorax and hemopneumothorax. [Diagram]. Retrieved by https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/human-lungs-pneumothorax-hemothorax-hemopneumothorax-1405120004
Mancini, M. (2018). Hemothorax. Retrieved from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2047916-overview
Pneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)
A pneumothorax is a collapsed lung caused by air between the lung (pleural space) and the chest wall. The air pushes onto the outside portion of the lung, forcing it to collapse. There are several causes of a pneumothorax: a motor vehicle accident, the insertion of a PICC line for medical procedures, COPD, cystic fibrosis, pneumonia, a ruptured air blister called a bleb. Ableb, a small sac of air between the lung and the outer surface of the lung, bursts and allow air to leak inside the lungs. Other causes of a pneumothorax includea mechanical ventilation malfunction, a knife or gunshot wound to the chest, asthma, and smoking. Just like a hemothorax, this too is a medical emergency.
Patients who present with a pneumothorax will have increased anxiety due to increased chest pain, increased heart rate, and rapid, shallow breathing. They may have shortness of breath. On assessment, health providers will hear diminished or absent breath sounds from the affected lung.
A chest X-ray and CT scan will be ordered. The standard treatment plan is to treat the underlying causes for a collapsed lung. Stabilize the patient by inserting a chest tube through the chest wall between the ribs. The chest tube will remain in place until the lung has re-expanded.
There is no way to prevent a collapsed lung, and people who have had a pneumothorax in the past may have another in the future.
References
Borke, J. (2019). Collapsed lung (pneumothorax). Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000087.htm
Logika600. (2020). Human lungs with pneumothorax, hemothorax and hemopneumothorax. [Diagram]. Retrieved by https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/human-lungs-pneumothorax-hemothorax-hemopneumothorax-1405120004
