What are bone fractures?
● Bone fractures are a medical emergency.
● A fracture is a break in the bone that can be small or thin or pieces of the broken bone.
● The severity of the fracture depends on the force that caused the break.
● A small amount of force to the bone can cause the bone to break or crack.
● Extreme force from a motor vehicle accident or gunshot can cause bones to shatter.
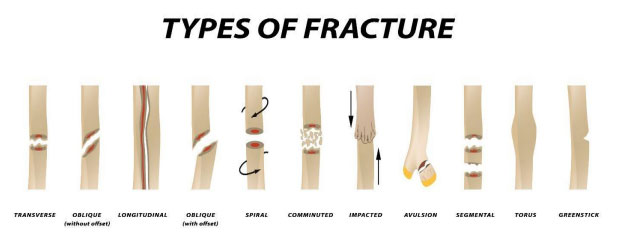
Types of bone fractures
1) Compound – Compound fractures (open) are serious fractures that occur when the bone fragments break through the skin.
2) Greenstick – A greenstick fracture is incomplete. The bones are broken but are not completely separated.
3) Transverse – A transverse fracture is a straight break across the bone.
4) Spiral – A spiral fracture breaks in a spiral fashion around the bone, caused by a twisting injury.
5) Oblique – An oblique fracture is a diagonal break across the bone.
6) Compression – A compression fracture is a crushed bone.
7) Impacted – An impacted fracture occurs when bones are forced together.
8) Communicated – Comminuted fractures break into three or more pieces or fragments at the site of the fracture.
9) Avulsion – An avulsion fracture occurs when a piece of bone, usually located in the ankle, foot, or wrist, is torn away from the ligament or tendon.
10) Torus – A torus fracture is typically seen in children when they use their hands to brace their falls.
a. The wrists absorb most of the impact and compresses the bony cortex (the dense, protective outer surface or the bone) on one side though the cortex remains intact on the other, creating a bulging effect.
11) Segmental – A segmental fracture occurs when a bone fracture into two places or floating segments of bone.
Causes
● Trauma from a fall
● Motor vehicle accident
● Contact sports
● Osteoporosis
● Overuse from repetitive movement that can tire and weaken the muscles and place more pressure on the bones
● Increased force applied to the bone that cannot be absorbed, weakest when twisted, or kicks to the body.
Symptoms
● Pop or snap felt or heard at the time of the injury
● Increased pain during movement or when pressure is applied
● Swelling
● Decreased range of motion in the area
● Warm, burning, redness in the injured area
● A bend or movement in a bone where the fracture occurred
● Deformed surface appearance at the location of the injury
● A bone puncture through the skin
Diagnosis
● X-rays
● Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
● Computed tomography (CT) scan
Treatment
● Determined by the type of fracture diagnosed from the diagnostic results
● Cast immobilization: functional cast or brace
● Traction
● External fixation
● Open reduction
● Internal fixation
Recovery
● Recovery time depends on the patients’ age, health, type of fracture, location, and severity, and other injuries that may be present.
Prevention
● Ways to prevent fractures from occurring: a nutrient-rich diet, increased calcium and vitamin D intake to strengthen bones, and integration of weight bearing exercises into daily routine.
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2021). Fractures (broken Bones). https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/fractures-broken-bones/.
Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Bone Fractures. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15241-bone-fractures.
Timonina. (2021). [Infographics]. Types of fracture. Fracture bone set. https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/types-fracture-bone-set-infographics-vector-1383154301.
