Have you ever had aggravating hip pain at bedtime while lying on the affected side of the hip or after getting up from a chair after sitting for a long period of time? Have you ever had hip pain that gets worse the longer you walk or the more steps you climb? If you answered “yes” to any of these scenarios, then you may have hip bursitis.
What is a bursa?
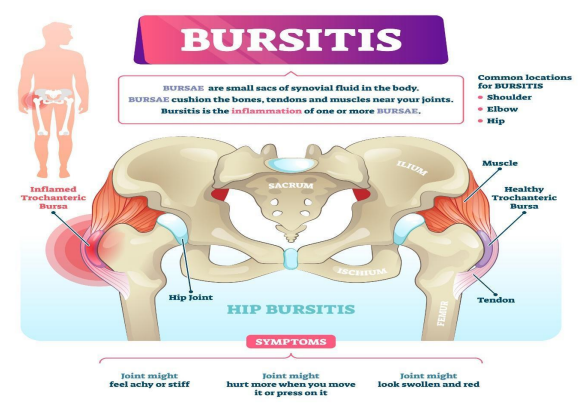
A bursa is a spongy, fluid-filled sac that cushions the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints (shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, heels, and the base of the big toes). The purpose of the bursa is to reduce friction between the joints and soft tissue.
Causes of bursitis
Unfortunately, when the bursa becomes irritated due to overuse of the joints via repetitive motion by constant kneeling, bending, running, cycling, and playing sports, such as football, soccer, hockey, and baseball, that involve cutting motions and the shifting of the body weight on the joints, the bursa can become inflamed or infected. This is called bursitis. In non-athletes, bursitis occurs more often in women and elderly people. This can be due to a previous hip-surgery, scoliosis, length of leg differences, rheumatoid arthritis, bone spurs, and calcium deposits in the joints.
Hip bursitis
Two types of hip bursitis:
- Greater trochanter bursitis. The greater trochanter covers the bony point of the hips. When inflammation occurs at the trochanter, it is called trochanteric bursitis. Patients may present with complaints of pain at the point of the hip that extends to the outer side of the thigh. They may complain of sharp intense pain that becomes achy and spreads across the hip area.
- Iliopsoas bursitis. Iliopsoas bursa is located on the inside groin of the hip and is not as common as trochanter bursitis. When the iliopsoas bursa becomes inflamed, patients will complain of pain in the groin area.
Treatment
Although bursa inflammation and pain present in different locations, both non-infectious forms of bursitis are treated the same. The best treatment plan includes rest, ice, and NSAIDs to manage pain and inflammation. When there is an infection in a bursa, the treatment plan consists of antibiotics, aspiration of the infected fluid, and possible surgery.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, please consult with your primary care physician or general practitioner.
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2020). Hip Bursitis. Retrieved from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/hip-bursitis.
Rosenburg, J. (2018). Hip Tendonitis and Bursitis. Retrieved from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/87169-overview#a5.
VectorMine. (2020). [Illustration]. Bursitis vector illustration. Labeled bursae synovial inflammation scheme. Bone and tendon illness and disease diagnosis. Retrieved from https://www.shutterstock.com/
image-vector/bursitis-vector-illustration-labeled-bursae-synovial-1482450590.