If you’re having difficulty elevating your arms above your head due to injury from repetitive motion, such as painting, weight lifting, sleeping on your arm for long periods of time, chronic rotator cuff tears, playing a sport (swimming, tennis serve, throwing a baseball/softball/football), or an attempt to prevent yourself from falling, then you may have rotator cuff tendinitis.
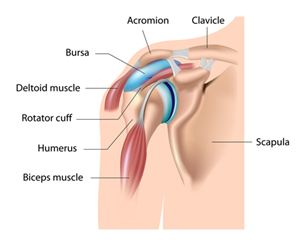
Rotator cuff tendonitis is inflammation of the four tendons that make up the rotator cuff. The tendons become more inflamed during increased shoulder movement. Patients will experience pain in the front of the shoulder, along the clavicle area and scapula.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, please contact your primary care physician for a shoulder X-Ray to assess the bone structure and an MRI or CT scan to assess soft tissue, tendons, fluid buildup (possible bursitis), and possible tears. Rotator cuff tendonitis is treatable with rest, ice packs and heating pads for 20 minutes four times per day interchangeably, and physical therapy. NSAIDS (Advil, Aleve, Naproxen, ibuprofen, etc.) are effective for managing the pain and swelling. Steroid shoulder injections may be effective. Depending on the results and the level of your pain, a referral to an orthopedic surgeon may be necessary.
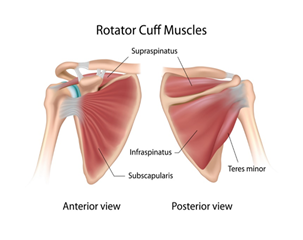
Shoulder Anatomy
The shoulder is formed where the humerus, collar bone (clavicle), and scapula join. The rotator cuff holds the humerus in place. The muscles that form the shoulder are the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, tres minor, subscapularis, and deltoid. There are four rotator cuff tendons and two biceps tendons that make up the shoulder.
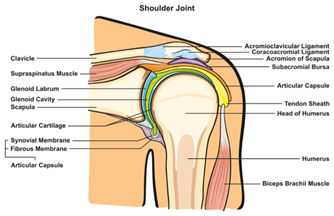
These tendons connect the deep layers of the muscles to the scapula and humerus, and provide support to the glenohumeral joint. The supraspinatus tendon is the most affected tendon due to overuse and trauma. The supraspinatus muscle is responsible for lifting the arms out to the side. An injury to this muscle can result in possible rotator cuff tear(s). Overuse can lead to shoulder (subacromial) impingement.
References
Alila Medical Media. (2019). Shoulder bursa, bursitis. [Illustration]. Retrieved from https://www.shutterstock.com/image-illustration/shoulder-bursa-bursitis-122298685?src=LgujqAxYpFEk2V8pW5kcBw-1-8
Alila Medical Media. (2020). Rotator Cuff Anatomy, Labeled. [Illustration]. Retrieved from https://www.shutterstock.com/image-illustration/rotator-cuff-anatomy-labeled-147943874
American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. (2019). Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Retrieved from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/shoulder-pain-and-common-shoulder-problems/NIH. (2019). Rotator Cuff Problems. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000438.htm
Udaix. (2020). Shoulder Joint of the Human Body. [Illustration]. Retrieved from https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/shoulder-joint-human-body-anatomy-infographic-699043855
