Discs (Intervertebral discs) are located between the vertebrae. They function as “shock absorbers”. With the help of the anterior and posterior ligaments of the spine, the disc allows flexibility of the spine and is responsible for the height of the spinal column. Discs are narrow in the cervical (neck) spine and progressively enlarge and thicken as they approach the lower back (lumbar). Collectively, discs are composed of collagen, fibers, and cartilage.
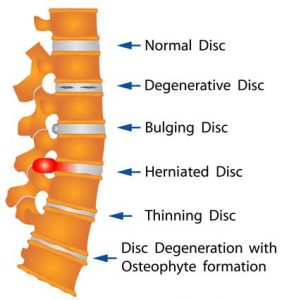
As we get older, our discs and joints wear down due to the wear and tear that we inflict on our bodies over time. The wearing down of the discs is called degenerative disc disease (DDD). However, degenerative disc disease (DDD) is not a disease, but it can be debilitating depending on its severity. DDD occurs when the discs, located between the vertebrae, lose their height (decrease in thickness). As a result, we become shorter. The wearing down of the discs can also create bulging and herniated discs that can pinch the nerves or sections of the spinal cord. Pinched nerves (nerve compression) can cause increased neuropathic pain and weakness depending on the location of the bulging disc or herniation.
DDD can also cause annular fissures, which are tears in the annulus (outer ring of the disc). This tearing can lead discogenic pain. Discogenic pain is pain that is caused by degenerative discs even though the disc may appear to be intact and functional. DDD can be seen on X-rays, MRIs, and CTs. Contingent upon the level of pain and severity, a referral to a pain specialist or neurosurgeon by your general practitioner or physician is needed for possible steroid epidural injections or surgical consult. Ice and moist heating packs four times a day for 20 minutes, spinal decompression, Medrol dosepaks, Gabapentin, Lyrica, and NSAIDs are effective for temporary relief.
References:
Cohen, S.P., & Malik, K. (2011). Discography. In Benzon, H., Raja, S., Liu, S., Fishman, S., & Cohen, S. P. (3rd Ed.), Essentials of Pain Medicine (pp. 462). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
Lotan. (2019). Spine conditions. Degenerative Disc. Bulging Disc. Herniated Disc. Thinning Disc. Disc Degeneration with Osteophyte formation. [Diagram].
