A hip fracture is a break in the upper portion of the femur (thigh bone). Most hip fractures occur in elderly people whose bones have become weakened by osteoporosis.
Hip Fracture
Esophageal Tears/Injury
Esophageal tears are caused by damage to the esophageal wall resulting from a mucosal tear, perforation, or rupture.
Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) and Cauda Medulla Syndrome (CMS)
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) and Cauda medulla syndrome (CMS) are neuromuscular andurogenital conditions caused by the pressing of lumbosacral nerve roots.
Flail Chest: Treatment, Symptoms, and Recovery
A flail chest results from severe blunt trauma to the ribs and chest in multiple areas and can be caused by a MVA in healthier patients.
Cardiac (Pericardial) Tamponade
Cardiac tamponade is a medical emergency that occurs when blood or a bodily fluid fills thesbpace between the heart and the pericardium (the sac that surrounds the heart).
Traumatic Thoracic Aortica Rupture
A sudden traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta is caused by blunt force trauma related to amotor vehicle accident (MVA), a fall, or a crushing injury.
Aortic Dissection
The aorta is a major cane-shaped artery that branches off the left lower chamber of the heart and is a is a major medical emergency.
Rib Fractures
Rib fractures tend to occur from traumatic falls. A chest X-ray to assess damage to the lungs and a rib series to assess fractured ribs are necessary.
SLAP Tear (Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior Tear)
Shoulder pain can present itself in many ways. You can experience numbness, along with dull, achy, tingling, electrifying sensations.
Shoulder Sprain (Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint Separation) and Shoulder Strain
More about Shoulder Anatomy; Shoulder Sprain and Shoulder Strain. Shoulder separation occurs after falling directly onto the shoulder with the arm.
Shoulder Fracture
A shoulder fracture can occur after falling directly onto the shoulder with the arm either tucked or restrained to the body.
Dislocation of the Shoulder
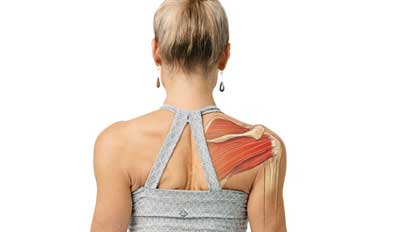
The shoulder is formed where the humerus, collar bone (clavicle), and scapula join. The rotator cuff holds the humerus in place.
Rotator Cuff Tears
There are two types of rotator cuff tears, partial and complete. Partial tears are incomplete tears that do not completely detach from the bone.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Learn more about Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis). Frozen shoulder pain and stiffness can progressively gets worse over time.
Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa. Bursitis is caused by overuse, trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and infections. Bursitis can also occur in the knees, elbows, and hips.
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Rotator cuff tendonitis is inflammation of the four tendons that make up the rotator cuff. The tendons become more inflamed during increased shoulder movement.
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs)
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are sudden and acute damage to the brain caused by a fall, motor vehicle accident, a jolt to the body, sports injury, blast (explosion) injury, or assault.
Shoulder Impingement
If you’re having difficulty elevating your arms above your head, then you may have a shoulder impingement, rotator cuff tendinitis, or a torn rotator cuff.