Have you ever wondered what type of injuries can occur from falling off a horse? A scapular, clavicle, and humerus fractures are all examples. Read below for information about these types of injury.
Causes
● Fractures can occur by falling directly onto the shoulder with the arm either tucked or restrained to the body.
● This type of injury usually occurs in male athletes who play contact sports such as football, rugby, wrestling, and mixed martial arts.
● Tears develop in the ligaments surrounding the AC joint, which is located between the acromion process and collar bone.
o When someone falls with his or her arm outstretched, the distal clavicle and acromion process may be fractured.
o Injury to the AC Joint can damage the cartilage within the joint, which can later cause arthritis in the AC joint.
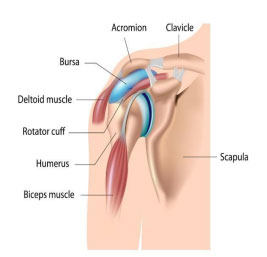
There are three types of shoulder fractures: scapular, clavicle, and humerus.
1) Scapular Fracture
● The scapula is the triangular bone located in the upper portion of the back.
● It connects the arm to the chest.
● Scapula fractures occur from severe direct trauma to the upper thoracic and scapular area.
● Scapula fractures are very uncommon.
Symptoms
● Symptoms include posterior shoulder and thoracic area swelling, tenderness, and bruising.
● Most of the time, when patients have a scapula fracture, they will have a severe life-threatening injury to their lungs, ribs, and nerves that will result in the scapular fracture treatment being delayed until the patient is stabilized.
o When the scapula injury is severe, surgery will be needed.
● Most scapula fractures do not require surgery due to minimal displacement and strong muscle support.
Treatment
● Patients will wear a sling for short-term immobilization.
● Once out of the sling and pain has improved, patients will be referred to physical therapy for progressive range-of-motion exercises until they have achieved full recovery.
● Most scapula fractures heal in 6 weeks.
2) Clavicle (Collar bone) Fracture
● The clavicle is the long bone that begins at the base of the neck and extends to the shoulder.
● Clavicle fractures are common.
Causes
● This injury occurs from trauma caused by falling on an outstretched arm or direct impact to the shoulder.
● Common causes include vehicle accidents and sports injuries.
Symptoms
● Hearing a snapping or cracking sound when the collar bone breaks.
● Front upper shoulder pain, swelling, deformity over the clavicle observed, one shoulder appears shorter than the other (one side drooping).
● Difficulty breathing or shallow breath sounds (indications of a lung injury).
● Vascular injuries such as a diminished pulse, swelling, decreased blood flow (venous stasis), possible blood clots (venous thrombosis).
Treatment
● If anyone exhibits any of these symptoms, please go directly to the ER for medical treatment.
o Labs (blood work) to assess arterial blood gases.
o X-rays of the clavicle, shoulder, chest (to assess pneumothorax or hemothorax), ribs.
o CTs to evaluate fractures and neurovascular injuries.
● Depending on the severity of vascular and pulmonary (lung) injuries, patients will be referred to either a vascular surgeon or a general/thoracic surgeon.
● Treatment for a clavicle fracture depends on the imaging results.
● Most clavicle fractures will heal without surgery.
● Wearing a shoulder sling may be necessary; however, not all clavicle fractures are the same.
● Fractures can occur in various parts of the bone.
o For example, if a fracture occurs in the middle of the clavicle, surgery is typically not required.
o If the fracture is medial, then surgery is possible, but may not be likely.
o If the fracture occurs laterally (near the acromion), then surgery may or may not be required.
o Patients will be referred to an orthopedic surgeon for a consultation for a possible surgical fixation.
3) Humerus Fracture
● There are two types of humerus fractures: proximal and distal.
● Proximal humeral fractures occur in older patients with osteoporosis.
o These fractures are often caused by falling while standing, falling down the stairs, or motor vehicle accidents.
o Patients with possible proximal fractures often complain of pain while moving their shoulder and elbow.
o Bruising and swelling of the affected shoulder and arm will be present.
o Most proximal fractures are nondisplaced and typically will not require surgery.
● Distal humerus fractures are associated with ipsilateral proximal forearm fractures.
▪ This type of fracture occurs in younger patients.
▪ Treatment plan
▪ Minimizing movement
▪ NSAIDS for pain management
▪ Ice compresses for pain relief and swelling reduction
▪ ER for evaluation
▪ Surgery based on the severity of the displacement
References
Alila Medical Media. (2019). Shoulder bursa, bursitis. [Illustration]. https://www.shutterstock.com/image-illustration/shoulder-bursa-bursitis-122298685?src=LgujqAxYpFEk2V8pW5kcBw-1-8
Frankle, M. (2019). Proximal Humerus Fractures. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1261320-overview